Progressive Tax? Why?
New Tax and Social System for a Fair Economy
Content
1. The traditional production factors
Table 1: Macroeconomic and microeconomic production factors
2. Problems of the Capitalistic Economy
3.1. First category Direct materials
3.2. Second category Direct materials
3.3. Third category Labor
Table 2: Commercial performance categories (with free prices and rents)
4.1. Direct materials
4.2. External services
4.3. Manufacturing licenses and other copyrights
5. The full performance of a company
Diagram 1: Individual Income
Diagram 2: Revenue of operating means
6. Commercial industries and public services
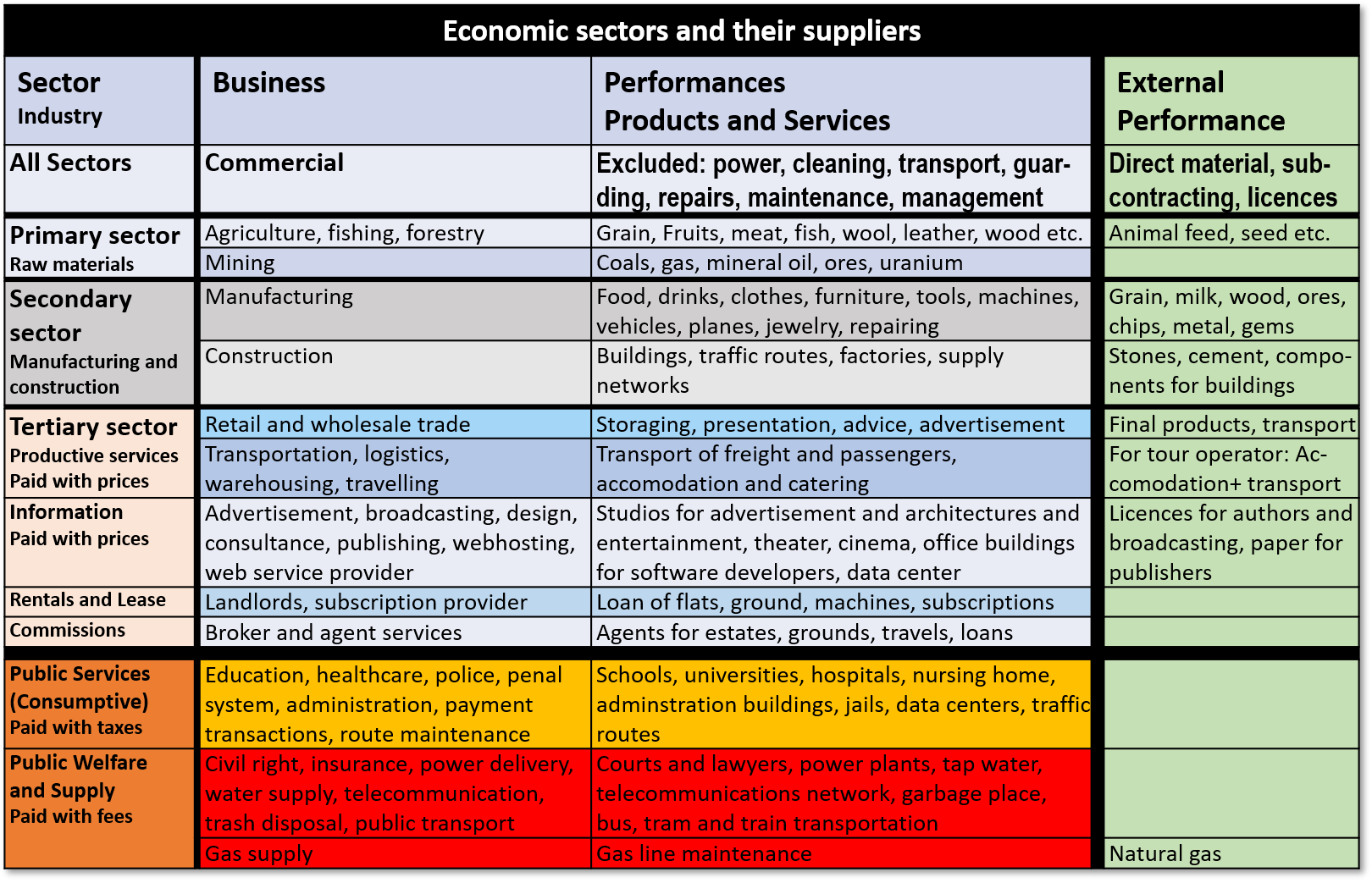
Table 3: Economic sectors and their suppliers
1. The traditional production factors
In the traditional economy all pupils and students learn about the production factors as elementary parts for every market economy.
One of the first prominent economists was François Quesnay (June 4, 1694, near Paris – December 16, 1774, Versailles). His book with the title Tableau Economique was published at 1759. He believed that all economic power depends from the agricultural sector. In his theory he divided economy in three classes, landowners, farmers and the sterile class. The manufacturers and traders were only consumers. That is why he recommended a single tax on ground rent. He was the first prominent economist who propagated laissez faire, laissez passé. The whole theory got the name Physiocrat. That derives from Greek words physis as nature and cratos as power. All prosperity depends from two factors:
- Land (nature)
- Labor for agriculture
His theories got a modern update through the American politician and economist Henry George (June 2, 1839, Philadelphia, USA – October 29, 1897, New York, USA). In his book Progress and Poverty published 1879 he described that a single tax on land would create a more just and productive economy.
At the next step more precise and successful rules were defined in a book written from Adam Smith. He was baptized at June 5, 1723 in Kirkcaldy in Scotland and died at July 17, 1790 in Edinburgh. His book An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations was published 1776. In his book he wrote about the main resources for the economy. These resources are:
- Labor
- Land
- Capital
He stated that taxation for the people should obey the four main principles of fairness, certainty, convenience and efficiency. The most fans of Adam Smith justify because of his canon of fairness, a progressive tax rate for the income of individuals. But the tax base of the income is defined with many deductions. In the private economy are the expenses for the means of production not part of the income. Additional in the private and the public sector are the expenses for insurance premiums deducted from the tax base. The ability or the performance of the taxpayer is not identical with the income.
The production factors of Adam Smith were added with the fourth factor entrepreneurship through the French economist Jean-Baptiste Say (5.1.1767, Lyon – 15.11.1832, Paris). He published 1803 his principal work: Traité d`économie politique. In his book he stated, that every company need the effort and knowledge and the skills of the entrepreneurs. They are intermediaries in the production process, who combine land, capital and labor in order to deliver a maximum for the needs of the consumers. He got the reputation of a leading protagonist of laissez-faire capitalism. In his volumes Cours complet d´economie politque pratiqe, published 1828-1829 Entrepreneurship was added to the former production factors.
Later the economist Karl Marx (5.5.1818, Trier – 14.3.1883, London) criticized the traditional economy. He divided the production process in several other production elements:
- Objects of labor
- Instruments of labor also called means of labor
- Labor (Labor power of subjects)
- Surplus value
He defined the objects of labor as a total of raw materials and auxiliary substances and intermediate products. The means of labor were buildings, machines, work-cattle, apparatus of every kind. He defined coal and water as auxiliary substances. They do not enter materially into the product. The coal is entirely consumed and only it’s value enters into the product, just as a part of the value of machine enters into it. In this case auxiliary materials, fuel, lighting gas etc., are not objects of labor, but instruments of labor.
The fourth element of the production process is the surplus value for the owner of the means of production as a total of the objects and the instruments of labor.
His books with the title Das Kapital were published in three volumes. The first volume was published at 9/14/1867, the second volume was published through Friedrich Engels at 1885 and the third volume at 1894.
In the modern, macroeconomic theory the production factors are:
- Labor with the reward of wages and salaries
- Land with the reward of rent
- Capital with the reward of interest
- Entrepreneurship with the reward of profit
As a justification for market economy economists tell still in modern times the metaphor of Adam Smith about the Invisible hand. The concept of the Invisible Hand mean, that self-interested individuals are not dangerous for the economy. In every trading business the provider and demander come together in order to change goods or services for money. Although both parties make their decisions because of self-interested intentions, both are winners if they use the opportunity to make an agreement with each other. This mean that a maximum of goods and services will be changed given and performed for a maximum of money, when no other than the seller and the client or the provider and the demander of a trade make a decision about the price or a rent of a deal.
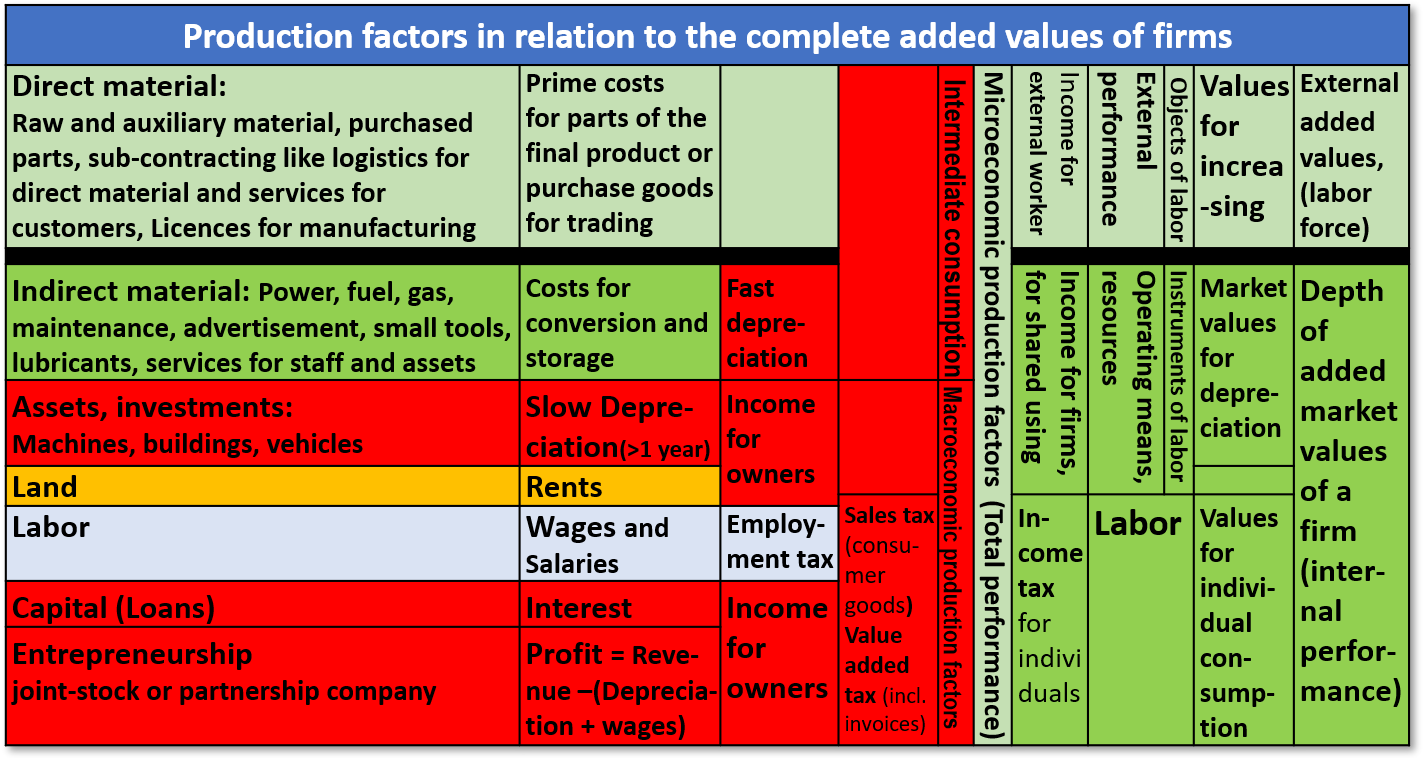
Table 1: Macroeconomic and microeconomic production factors
2. Problems of the Capitalistic Economy
But not all economists are satisfied with these theories. They criticize that the distribution of money between capital and the employed people is working with other rules than the distribution of tangible goods and services. The agreements between the employer and the employees are with other rules than the distribution of commodities and services depending on prices. The factor market with factor pricing obeys other rules than the product market with product pricing. The capitalists are a small minority in relation to the employed workers. They are rich and make profit because of the performance of all employed workers. The workers and the unemployed people are competitors for jobs. They all need the jobs for a regular income for themselves and their family.
But the owners of enterprises hire workers never for their full value, because they want make profit. Therefore they calculate the wages and the salaries lower than the true value of employees.
The wage of the owners can depend from their performance, if they are partner in a partnership company. But it is also possible, that they are only shareholder in a stock corporation. Then they claim their profit without any efforts.
A second reason why capitalistic economies get criticism is, there are no rules for the limits of private ownership. How is it possible to find a fair wage for firefighters or a fair price for their services? How is it possible to find fair salaries for physicians or the services in a hospital? How is it possible to find a fair salary for teachers or the services in a school or for the salary of police men and their services? How is it possible that the enterprises for public power supply and their clients make fair agreements?
Unemployment is a normal accompanying phenomenon in an economy with capitalistic distribution of money. But the ways and methods of governments to reduce unemployment are very different. The most of them prefer deficit spending of the state budget, in order to get more jobs in the country. Others prefer the privatization and capitalization of public services like the public railroad services or the public telecommunication.
Many modern politicians and economists think, the billionaires are necessary, because they create new jobs for the working poor and prevent so many people from the destiny of unemployment and homelessness.
There is a consensus between the most politicians and economists and capitalists and the leaders of labor unions that growth is the best way for reducing all economy problems. Growth of the gross domestic product, will give everybody more purchasing power. In the consequence the demand will increase and the firms get more orders. In this case all politicians and economists and all employers and the employees are convinced to be winners.
But in the real life it’s a dream to get all the time an economic boom. That’s a dream like to get more performance with the help of drugs. In the reality after the economic boom follows the economic depression. Usually such effects can be veiled with the assistance of banks and their loans and security exchanges.
The expectation of more fiscal policy and monetary policy and a better tax policy are still existing and the combination of all is the task of the specialists of macroeconomic measures. It’s no surprise that such actions are very complicated and the scientific rules about these topics are not accepted from all people. One of the side effects of fiscal and monetary and tax policy is a permanent inflation rate of the consumer prices.
People with many assets but only a little savings think, that inflation is necessary because of the purpose, to increase the demand for goods and services. But other people with less material assets and high savings learn, that their savings melt down through inflation and they get the experience, that they need as a pensioner the pensions of the government all the time of their life.
An economy with macroeconomic policy is in every case an economy with deficiency. Enterprises with the need to share the result of their performance between the employees and the employer need often the support of banks. Then they have to calculate additionally to the profit of the shareholders the interest to the banks because of the loans. The interest and the profit are factor costs in order to avoid insolvency. Employers and employees are opponents because both classes claim their part of the revenue of a firm with different reasons. The members of both classes want reduce the share of the other class in every case.
There are many reasons for increasing of alternative economic concepts. The theories for government intervention in economy are known under the name of the visible hand. They justify macro-fiscal policy for more employment. In the 1930s John Maynard Keynes (5.6.1883, Cambridge, United Kingdom – 21.4.1946) and other economists searched for remedy of the shortcomings of capitalism. They argued that the Great Depression was more than a flaw, it was a failure of the market economy. Deficit spending of the government in order to stimulate the growth of the economy was a preferred method to stabilize the demand of goods and services in the national economy. The budget of the government should be an instrument, to guarantee a perpetuate and steadily flow of the money in a market economy. Hence the government should handle a compensation or a countercyclical money policy caused through the cyclical depressions on the capital markets. They knew, that the purchasing power of a national economy depends from the bull and bear markets of the stock exchanges.
3. Microeconomic perspective
We need a new perspective to the production factors. That means a complete consideration of all production factors are necessary. In the first step it is helpful to learn something von Erich Gutenberg about the microeconomic production factors. Erich Gutenberg was born 12/13/1897 in Herford and died 5/22/1984 in Köln, Germany. In his book with the title Die Produktion Grundlagen der Betriebswirtslehre published 1951 he divided the microeconomic production factors in the three categories Arbeit as labor, Betriebsmittel as operational means and Werkstoffe as direct material.
He made a comparison of the microeconomic and the macroeconomic production factors. The microeconomic production factors are parts of the total performance of a firm.
His production factors are:
3.1. First category Direct Materials
The first category direct materials are necessary in the production process for the fabrication of new products. They are not consumed, because they go as components into new products. Direct materials are manufactured from other firms. The main feature of direct materials is that they are produced with the performance of supplier companies.
Therefore direct materials can be raw materials or small auxiliary materials or purchased parts in case they become a part of a final product. In case the products are purchased for trading, direct materials are even finished products.
3.2. Second category Operational Means
The second category of microeconomic production factors are operational means or operational resources. Such things are necessary for production, but they don’t go into final products. These things are indirect materials or equipment for the production process. That mean their value will decrease in the company. It’s possible that the decrease of the market value will be very fast or slowly. For example, the use of electric power or energy materials like fuels, coals, natural gas lose their value instantly in the production process. Such things deliver the energy for intermediate consumption. Lubricants are necessary for the running of many machines and operational means. But buildings and machines are additional necessary. They lose their value more slowly. For their depreciation is at least one year necessary. The third part of operational means is land. This category is without any depreciation. But for a friendly or an unfriendly purchase of a firm the speculators have to calculate all assets of a company.
3.3. Third category Labor
The third category of the microeconomic production factors is labor. This factor is like the macroeconomic production factor labor. The wages and salaries for the employees are necessary for any adding of market values in a company. It’s the income for individuals and often burdened with different types of progressive tax or even with flat tax rates.
4. Performance categories
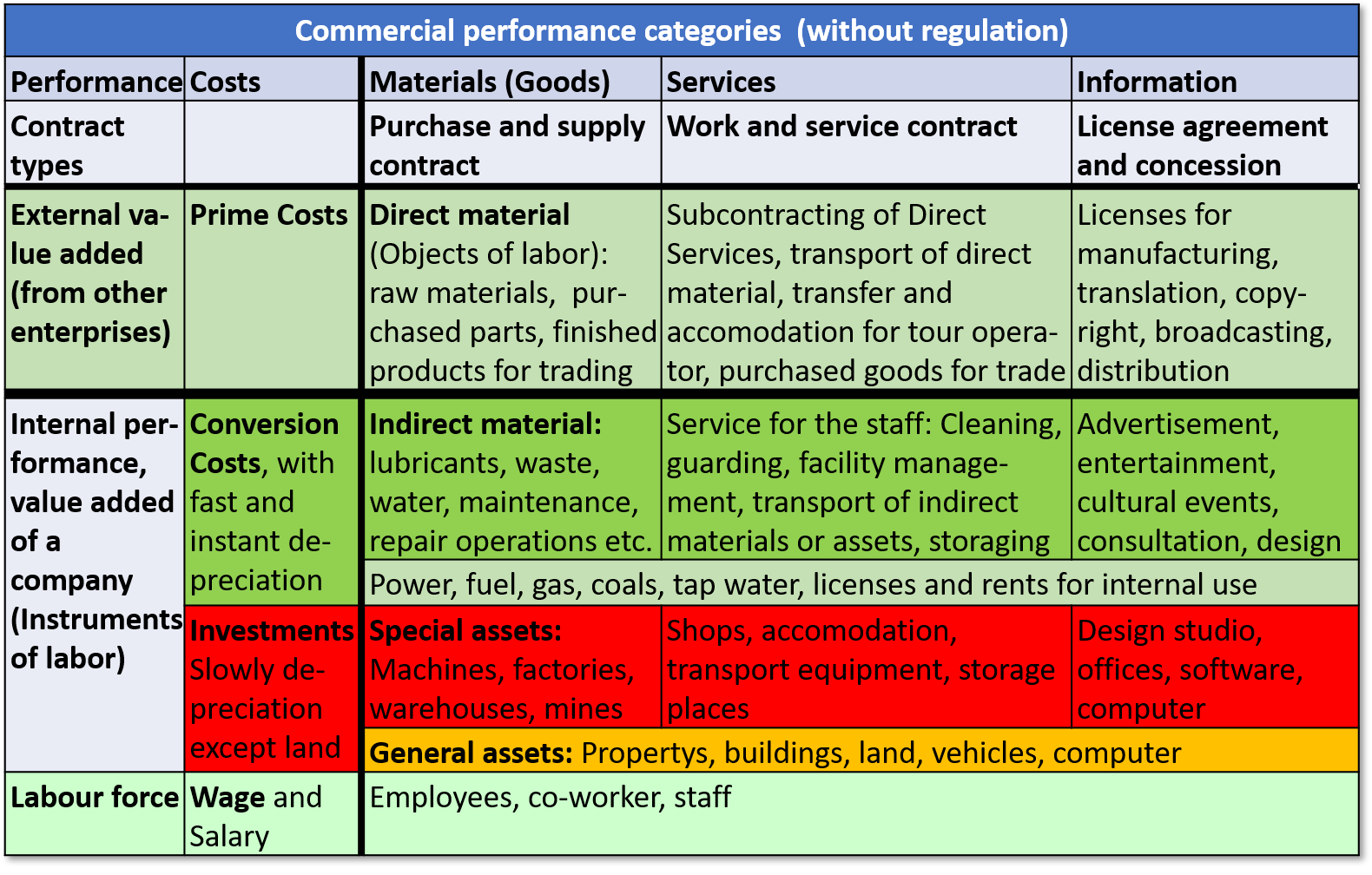
Table 2: Commercial performance categories (with free prices and rents)
4.1. Direct materials
In the next step we describe the characteristics of the microeconomic production factors for the branches who get their sales revenue through prices or rents. Then we need a concept including goods and services and even the copyright. It is in all categories necessary and possible to separate the performance of a firm from external performance of the suppliers and the subcontractors and from the owners of manufacturing licenses.
In order to separate external performance from the internal performance of a company, firms have to collect and add all invoices for direct materials. Directs materials are tangible things who increase their value in the production process because they will be converted into parts for final products. Such materials are often raw materials or purchased parts for new products. For traders it’s easy to calculate external performance, because the purchased prices of all sold goods have to be subtracted from the sales volume in order to get the internal performance. The sales volume is the total of internal and external performance of a trading company. Hence the total of the purchased prices of the sold commodities is the external performance of the trading company.
But the most rules are with exceptions. Is electricity tangible material? Is it direct material?
Electric cars need rechargeable batteries and flashlights need batteries too. Hence electric power can be sold with batteries. Then it is direct material for the producer or trader. But the energy for the production of cars or flashlights are a part of the operational means. The same is evident for other energy materials. If coals are sold in sacks or gas in gas bottles or fuels at petrol stations, it is direct material for the trader. Otherwise such energy materials are operational means for the company.
4.2. External services
The trading company is a service provider who storage products for sale and make advertisement, consulting, cleaning and guarding of his commodities. But even in the industry the firms have to pay for services which are part of the value chain. The factories need direct material in order to create new products. The company can purchase direct materials when it stores on the area of the supplier company. But it’s also possible that a company pay a higher price for direct material, because the transportation costs for delivery from the seller to the buyer is included in the purchase contract.
In this case there are two options. Either the seller will perform the transport service or a logistics company will execute the transportation because of a subcontract. Therefore the service for direct materials is added value for direct materials. That mean the transportation of direct materials is external performance in the production process.
That’s different to services for machines and instruments and tools of a company. Such equipment is property of a company. They need maintenance and repairs and the buildings need renovation. The services for the property of a company are either for the final products nor for the clients of a company. They are not services of subcontractors. Such services are not external performances for a service provider or in the production process. Another example is the service of a tour operator. They sell often complete journeys. Mostly they own no hotels and no buses and no trains and no airplanes. Despite of this fact they can fulfill all services for a complete journey, because the value of the travel contract contains subcontracts for transportation and accommodation and catering. Such services are not for the property of the tour operator, but for clients of the travel company.
4.3. Manufacturing licences and other copyrights
Some companies bought a patent or a license in order to get the right for manufacturing. In other cases, they have to pay authors of books in order to get the copyright for duplication and reproduction of books. Television companies have to pay for the right to broadcast sport events and other happenings. Movie theaters have to pay for the right to stage films from the companies of the creators. The motion picture companies need the revenue, because they have to pay the movie actors. At such cases the firms get their revenue with the need of the permission of the owners of intangible and immaterial properties. If the creators or owners are not employees, external performance is part of the value chain.
5. The full performance of a company
The separation of the total revenue as total performance of a company into external performance and internal performance is possible and necessary. But the professionals of a firm have their options. Do they pay for direct materials or for external services or for the rights of using immaterial property? In every case they are able to calculate the total performance of a company. Why is such a separation necessary? Is it a way into more bureaucracy?
The calculation of the full performance of a company is not necessary as tax base for additional burden of the employees of a firm. It is a substitute for other needs of a capitalistic tax system. Other values like the capital gain or the market value of companies or the distribution of profit is no more important. Only the complete tax base for a fair tax system is essential. All added values are created because of the performance of the employees. If the government want pay for a basic income unconditionally, it has to burden the full income with a direct tax. Direct tax mean, not one object is the tax debtor of a firm, but one or many subjects of a company are the debtors of the tax liability!
When not an object, but one or many subjects are the debtors, it is possible to create a progressive tax rate instead of a flat rate for calculation of the tax amount. Self-employed persons and employees have no deductions from the tax base. But on the other hand, the full tax amount will be reduced with a basic income for both. Social transfer income and tax burden are without restrictions for all.
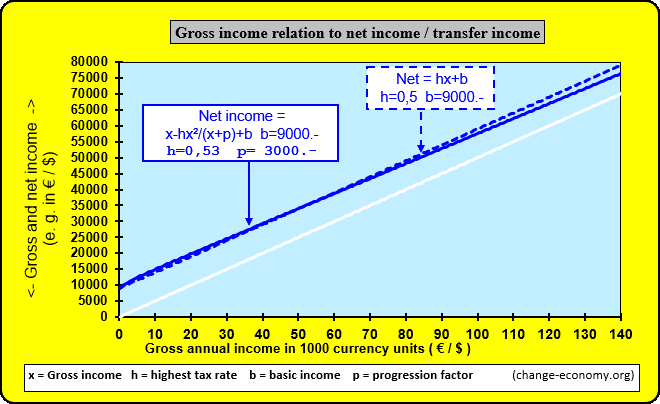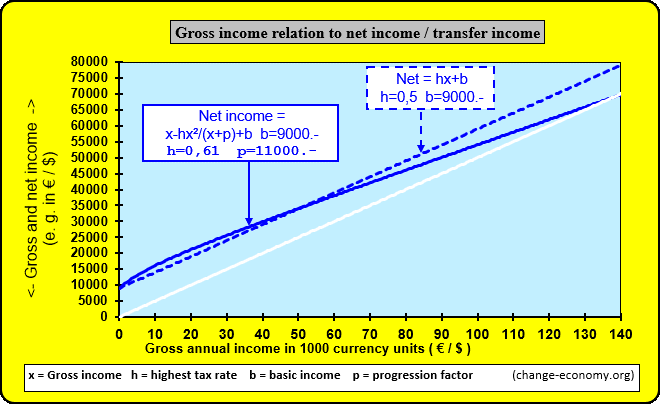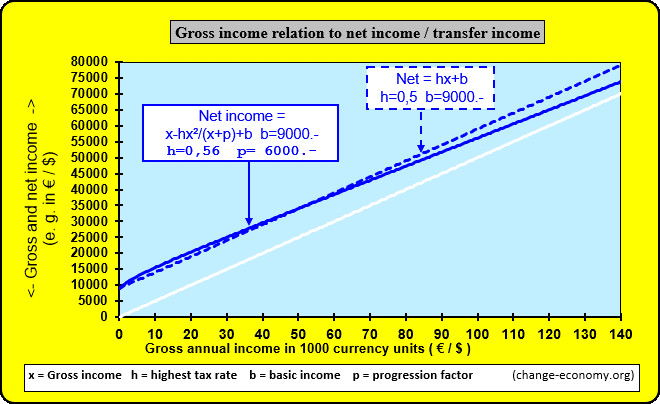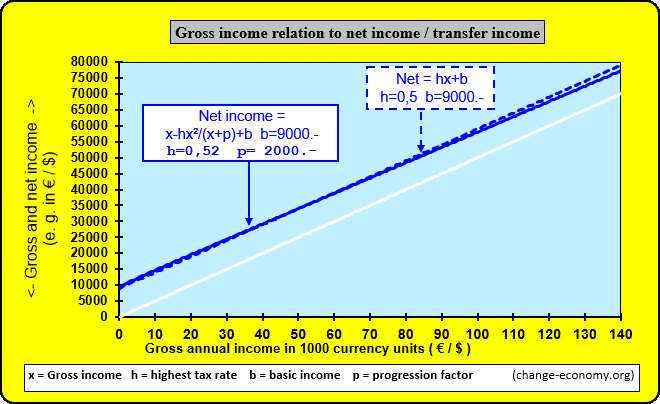
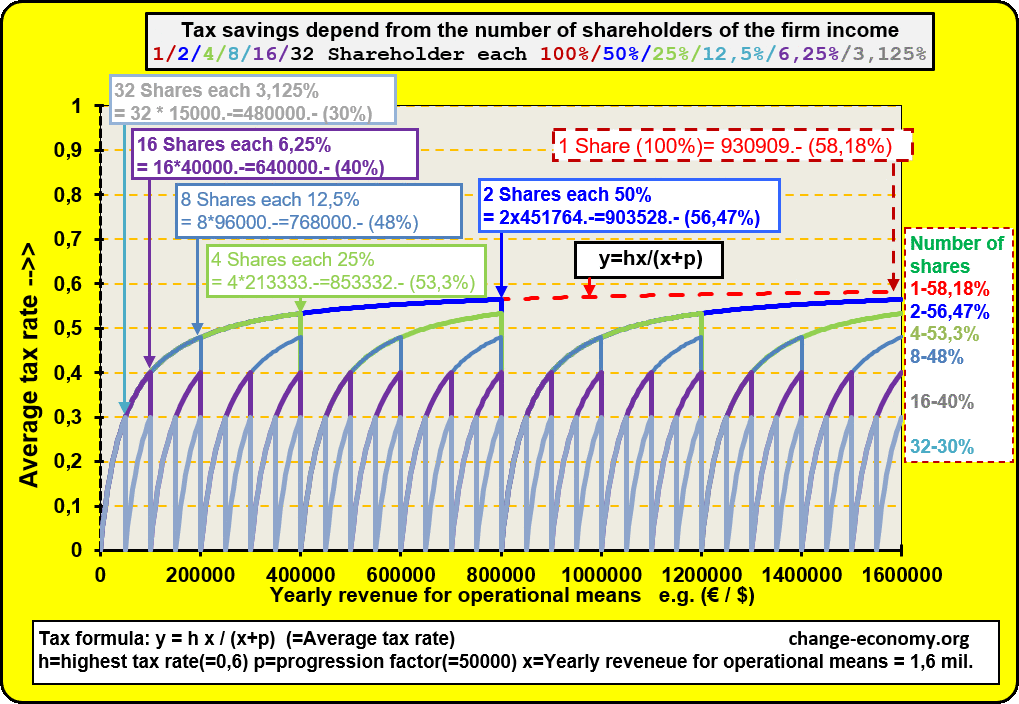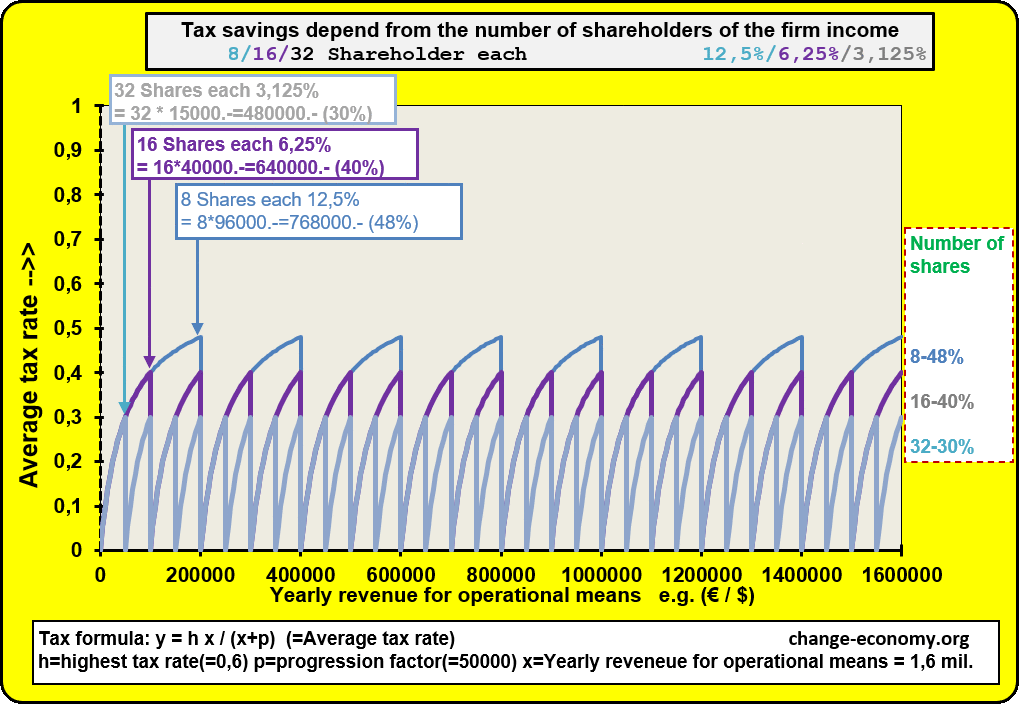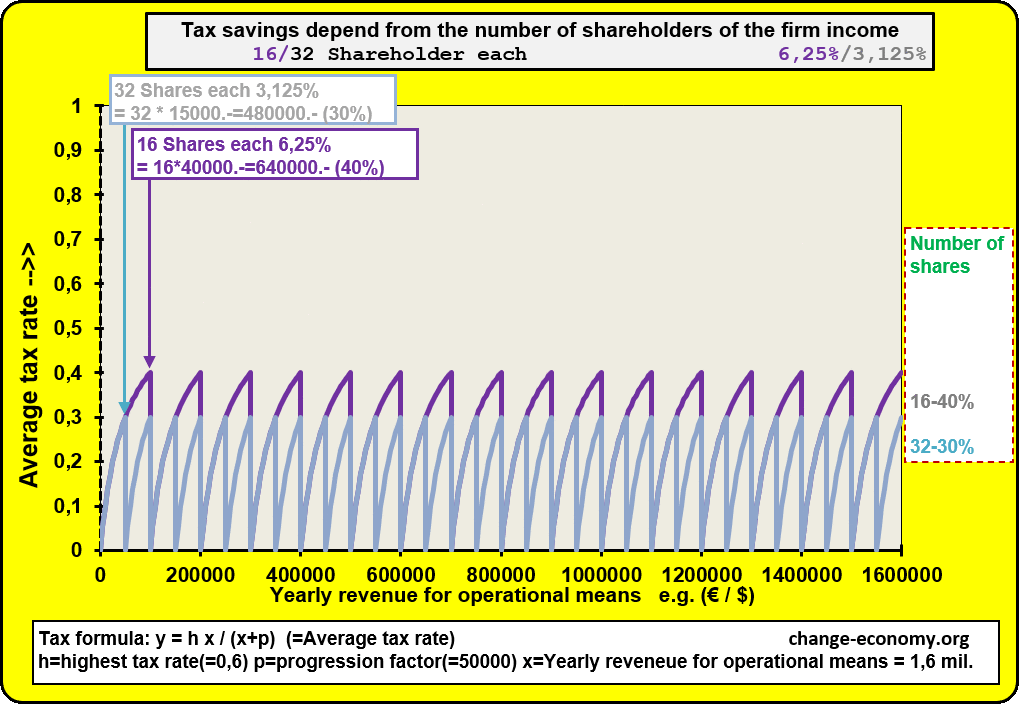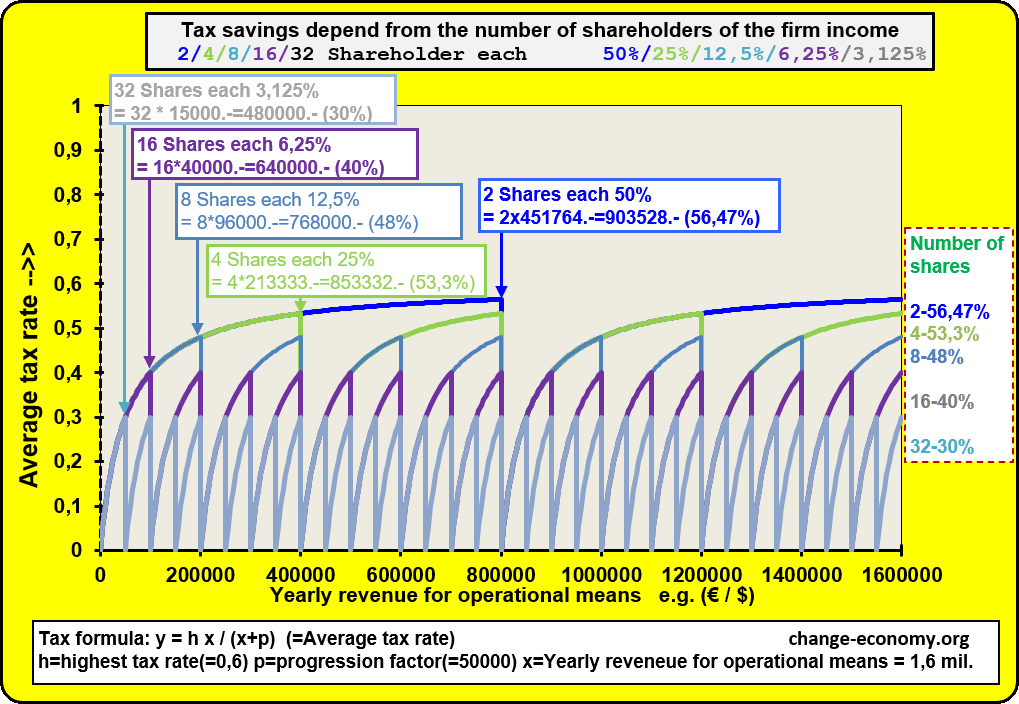
Diagram 1: Individual Income
In case the firm of a self-employed person is growing, he will hire employees in order to satisfy all demands of clients with suitable supply. In the consequence the owner of the operating means has to pay more and more equipment and indirect materials with his income. Because of a progressive formula of the tax the percentage of the average tax burden is growing too. Then it is a problem to offer competitive prices in comparison to other providers. Now he has the option to found a company. Then the added values of the company will be divided in two intended purposes. One part of the income is for distribution among individuals. The individuals get the money as wage or salary. The other part of the income is for the operating means of the company. The company has at least two shareholders. The shareholders don’t have a fix part of the assets for taxation. They participate of the income of a company, because they have a fix share of the company income. They have no option to avoid progressive burden or to get tax deductions. But they can distribute the tax burden on more shoulders. Only employees have the option to get shares of the income of a company for common use.
Diagram 2: Revenue for operating means
If somebody leave the firm because he will retire or he change the company or any other reasons, he will lose the duty to pay tax for the old company in every case. Because of this condition, every company has at least two shareholder and at most all employees are shareholders of the company income. Hence it is an advantage for all shareholders, if they give new employees shares on the company income. It’s not necessary that new shareholders have to pay deposits at the beginning and later if they retire, they can’t claim an amount, because of the end of partnership.
The existence of a company has more priority than the division among the shareholders. But there is an exception. If the liquidation of a company is not avoidable, it is necessary to calculate the shares of the assets. In this case it is possible that the shares of many eliminated shareholders are depreciated. Then it’s necessary to evaluate the shares even of eliminated shareholders. The value of shares in assets depend from the duration of membership in a company. For eliminated shareholders the value of shares in assets depend additional from the duration, since they paid no more for the company. Newcomers can’t make profit and retired shareholders of the company income lose their claims of the assets only gradually, because of depreciation. The calculation of the shares of the company income is necessary for taxation. The calculation of the shares of the assets is only necessary for liquidation, in order to divide the values for distribution between the shareholders in a fair manner.
6. Commercial industries and public services
The table of the commercial industries are separated in in three sectors:
- Primary sector: Production of raw-material as commodities
- Secondary sector: Transformation or conversion of materials in final products, Construction of buildings and public property
- Tertiary sector: Services. They are divided in different types of payment
Table 3: Economic sectors and their suppliers
In the traditional economies there are permanent controversial discussions about private ownership and governmental ownership of operational means. There are many political parties who wrote their special opinion about public and private ownership in their programs. It’s a traditional reason for the founding of new ideologies and for demarcation to other political parties. The discussions about banks and assurances and financial fonds and securities exchanges seems to be a never ending story.
But for us it has no priority to discuss either the consequences of private money creation nor the consequences of deficit spending of the governments.
It’s more important to learn something about the different types of service providers in every economy. The differences depend not from mentality and not from the language of the people. It’s important to know something about the kind, they are paid from the people. They all get their money in five different types.
- Prices – for example trading companies, tour operators, cinema, advertising etc.
- Rents – for flats, safes, webhosting, broadcasting, fitness center, machines, land for individual use etc.
- Commissions – for brokers and agents for real estates, credits, ground, travels etc.
- Taxes – for universal education, health care, criminal law, route maintenance, police force
- Fees – Power delivery, tap water, telecommunication, civil right, insurances, public transport, trash disposal, pipe gas, land for public use etc.
When we analyze these differences, then we should understand that private and public ownership are necessary for every modern economy. Both have their entitlements. But it’s not necessary to make for service provider a mixture of public and private partnership. It’s in times of capitalism only an ideology to sell the operating means for public services to billionaires and oligarchs and investment fonds in order to reduce the public debt. In such times nobody can imagine, that private companies can exist without cancellable loans and without securities exchanges.
In order to establish a fair and sustainable economy, it is a serious condition to create a tax law who burden all revenue of persons without exception. And all the income of a persons has to be burdened in a progressive manner.
7. Outlook and Forecast
A big question are all the consequences of a substantial reform of the money and transfer system. How many effects of the reform are calculable? A main feature of the new tax and social system is a basic income for all people. That does not mean, all people get guarantees for the same income. The basic income depends from the age of the people. Children are economic dependent from their parents. Hence the parents get a surcharge for every child. But for adults it’s possible to calculate a basic income, anyway if they are students or working in a job or at home for the family.
The main objection against a basic income is the argument, that a basic income is too expensive. In a capitalistic way of money distribution, the employees have to work for themselves and for their families and for the property and the profit of the capital owners and for the unemployed people and for the health system and in many countries for the profit of the owners of the health institutions. The money of the income tax is definitely not sufficient to pay all the civil servants and all the public infrastructure and the transfer income of the unemployed and of the profits of the owners of the public and private institutions. Even if the employee tax is added with a value added tax or a sales tax, the governments revenue are not enough for paying a basic income.
Hence a new tax system is necessary. Participation is no more an ethical or a morally question of capital owners with a special education. Co-determination and participation are the only methods for every company owner with employees, to reduce the tax burden. The more workers have shares of the income of a company, the lower the tax burden is for the company.
Then the money distribution is an internal matter for all companies. Trade unions and employer associations or other external associations can help no more a company. Strikes and lockouts are counterproductive in every case for a company. The workers and partner of a firm have no more the need and the option to pay the wages and the salaries with credits of a bank.
But for investments the companies have still the option to pay only a part with cash. Because of the market value of investments, some of the assets can be securities for pawn loans. In this case the value of the loan is calculable for the whole term of a loan. The value of the loans will be calculated with a price, because the contract is not cancellable through one party. A premature termination of a loan is only possible with a repurchase of the credit. Hence a company has no more the burden either of the profits for the owners nor the interest rates for the creditors. Such conditions for loans are possible, if a government is able to guarantee a stable price level of the consumer prices. The governments are responsible for the money supply through the revenues and the expenses of the state budget. They have to balance the revenues and the spending. This is possible, in case economic depressions and unemployment and the claim of deficit spending is finished. The governments and the firms will be independent from stock exchanges and trades unions and employer associations. The companies are no more forced to grow in order to get full employment. For all people, who search a job are enough jobs available, even in a shrinking economy with shrinking wages.
In a modern economy are many investments for the protection of the environment necessary. Governments make new laws in order to guarantee more sustainability in the economy of their country. Then it’s necessary to establish stable companies. Such firms need no more distribution struggle and no oligarchs and no unemployment for a sustainable production process. They have and offer enough working places, even if the burden for the environment is growing. The governments have no more the alternative either to damage or even to destroy the economy or the ecology.
Basic and unconditional income with capitalism is indeed a method to move an economy in poverty. But with an unconditional taxation of the whole performance of a company, it’s a way to guarantee all workers the same conditions and to guarantee all unemployed people the same rights.
A further advantage of stable firms, it’s no more necessary to give the public property to oligarchs. The organization of the healthcare and the penal system and payment transactions and route maintenance and general knowledge is possible, without competition. If such tasks will be organized with a solidaric management, the costs for the country will be lower and the quality level will be higher, than otherwise with many regulation laws and many low wage jobs.
Many other public services will not be performed through the tax payer. For the supply of tap water, electric power, public telecommunication, public transport, trash disposal, insurances or the service of civil right people have to pay different types of fees. The citizens have no chance to get individual prices for such deliveries and services. Hence it is better, to sell the properties for such services not to oligarchs. It is cheaper and with a higher quality level for the population, if the infrastructure and the buildings for insurances will be managed and maintained through the government or communities or city administrations. In order to avoid a privileged class for profit skimming and a lower class for low wage jobs and in order to avoid unemployment, it is necessary, to avoid a mixture of ownership for the same services.
In the future it’s common sense to divide the service industries in two main categories. One category for the market and one for the government. One category for the invisible hand of private competition and one for the visible hand of public organization.
1. In the first category are all productive services. These services are paid with prices or rents or commissions. They will exist in private ownership and they provide their services in competition with other service providers.
2. The second category are all consumptive services. Such services will be paid with taxes or with fees. The best quality with the lowest costs for the society of a country comes true, if they are offered in a solidaric organization without competition.
Public private partnership as a method to create new jobs, through the profits of the owners in order to reduce unemployment is not a permanent solution. We need an economy without crisis, with a continually thrive and in peace with the ecology. The goal is a sustainable economy, who can exist with enough protection for the environment. Therefore we need a tax system, that reward all companies through participation of their employees. Such a tax system is possible in addition to a transfer system, which can guarantee all people a basic income.
An additional important advantage of the new money system will be, that the people of a country can establish more stable democracies. They have no more to share their power either with oligarchs nor with parties. They can vote for their representatives in the parliament or in the government without preselection through preelection. The last decision of controversial questions between the state authorities will be solved with a referendum.
®